Professional and Ready-to-Use 7+ Project Estimate Templates for Every Industry
A project estimate serves as the compass guiding the journey from concept to completion. Like a skilled navigator, a meticulously crafted estimate anticipates the twists and turns of the project terrain, offering a clear path forward while acknowledging potential detours. It’s not merely a number but a narrative of possibilities, a story of what could be achieved within the constraints of reality. A robust project estimate is a cornerstone of effective management, grounding aspirations in practicality and fostering informed decision-making.
Our Project Estimate Templates in MS Word format are like ready-made blueprints for your project’s costs and timelines, designed to make your life easier. Whether planning a construction job, a tech project, or a marketing campaign, these templates are flexible enough to fit your needs. With easy-to-use features, you can quickly fill in your details, break down costs, and create professional estimates without any hassle. Say goodbye to tedious calculations and formatting issues – our templates are here to simplify your estimation process and ensure your projects stay on track.
Why Accurate Project Estimates Are Crucial
Accurate project estimates are vital for successful management:
- Budgeting: Ensures projects stay within budget and that resources are used efficiently.
- Resource Planning: Helps in allocating manpower, materials, and equipment effectively.
- Risk Management: Identifies and plans for potential risks, avoiding costly delays.
- Client Expectations: Set realistic expectations and build trust with clients.
- Decision Making: Provides data for prioritizing tasks and adjusting plans as needed.
- Success: Forms the foundation for well-planned and executed projects, leading to successful outcomes.
In conclusion, accurate project estimates are essential for effective management. They help in budgeting, resource planning, risk management, client expectations, decision-making, and overall success.
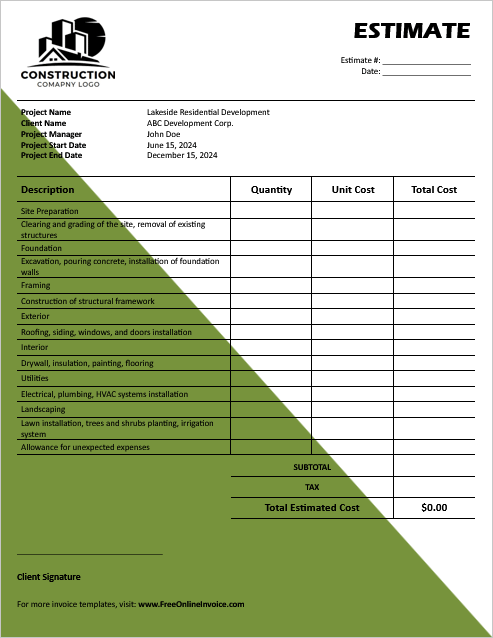
01. Construction Project Estimate Template
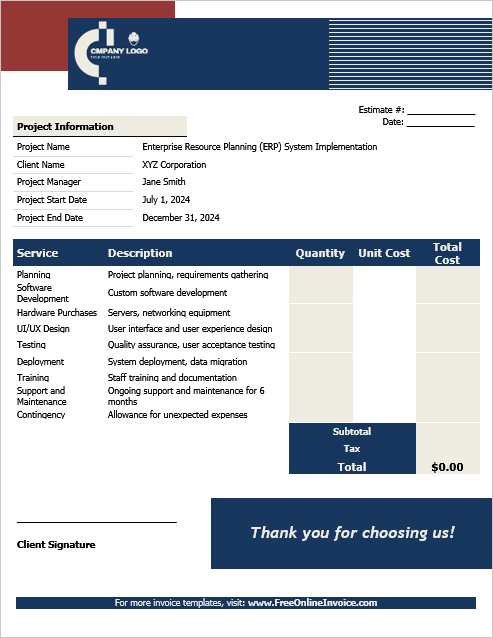
02. IT Project Estimate Template
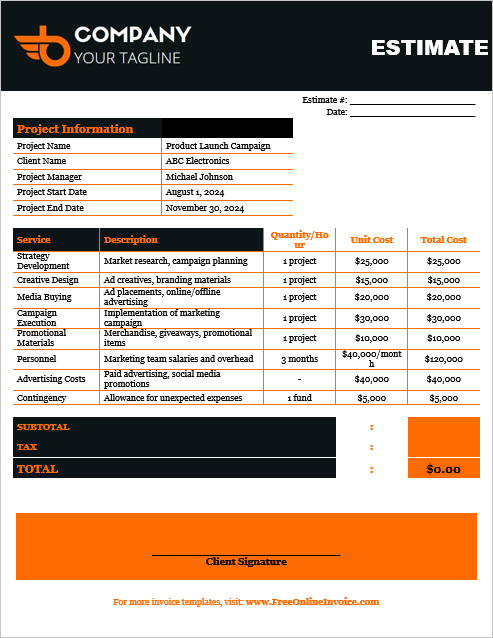
03. Marketing Project Estimate Template
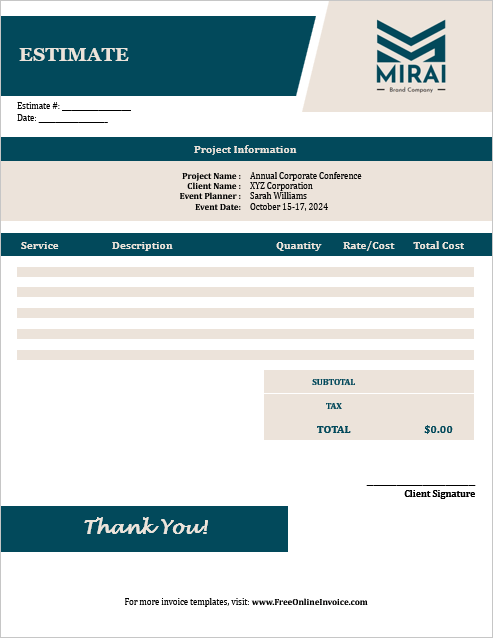
04. Event Planning Project Estimate Template
05. Software Development Project Estimate Template
06. Interior Design Project Estimate Template
07. Engineering Project Estimate Template
Project Estimation Techniques:
- Analogous Estimation: This technique relies on historical data from similar past projects to estimate the current project’s duration, effort, or cost. It’s quick and easy but may lack accuracy if the current project differs significantly from past ones.
- Parametric Estimation: Parametric estimation involves using mathematical models and statistical data to calculate estimates based on specific parameters, such as cost per unit or duration per unit. It’s more accurate than analogous estimation but requires reliable data and assumptions.
- Three-Point Estimation: Also known as the PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) estimation, this technique uses three estimates for each task: optimistic (best-case scenario), pessimistic (worst-case scenario), and most likely.
These techniques offer different approaches to estimation, each with its strengths and considerations.
Estimation Accuracy Metrics:
Measuring how accurate our estimates are is like checking if we hit the bullseye or missed the mark. One way we do this is through variance analysis, where we compare what we thought would happen with what actually happened. If we did better than expected, that’s a positive variance. But if we fell short, that’s a heads-up that something might be off. It’s like looking back at old road trips to see if we’re getting better at predicting how long the journey will take.
- Variance Analysis: Compares estimated values with actual outcomes to identify deviations.
- Historical Data Comparison: Compares current estimates with past data to spot trends.
- Feedback Loop: Regularly reviews and updates estimates based on real-world outcomes.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involves stakeholders in the estimation process for realistic estimates.
← Previous Article
« Comprehensive Cleaning Estimate Templates: 6+ Free Downloads



